About Radon
WHAT IS RADON AND WHY IS IT DANGEROUS
Radon Gas
Radon is a colorless, odorless, radioactive gas that occurs naturally. It is able to leak into houses and other structures. Long-term exposure to high radon levels increases the risk of lung cancer.
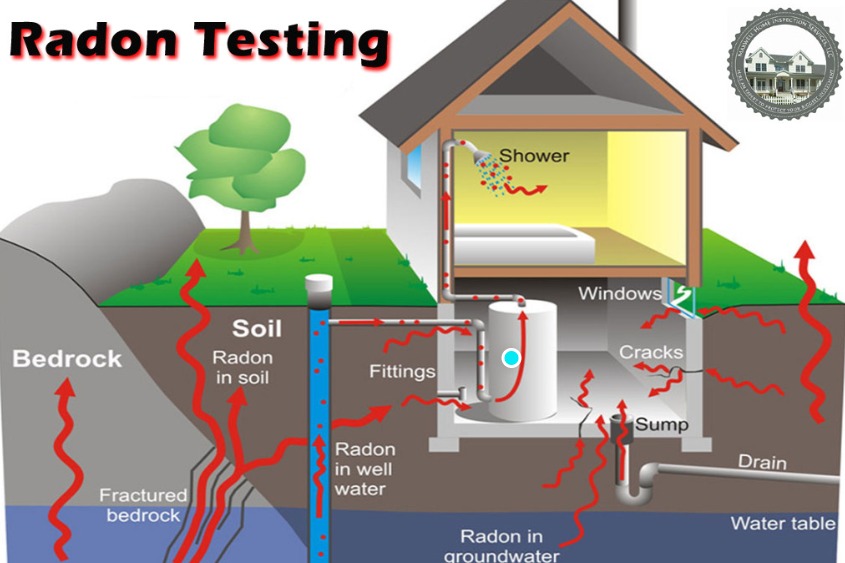
From where does Radon Gas originate?
When radioactive metal (radium, thorium, or uranium) decays in rocks, soil, or groundwater, radon gas is naturally produced. Because it evaporates and vanishes outside, the levels are low. However, radon gas can infiltrate indoor spaces through the foundation of structures and get trapped. In their homes, schools, offices, and other indoor spaces, people may inhale radon gas.
How does the body react to radon gas?
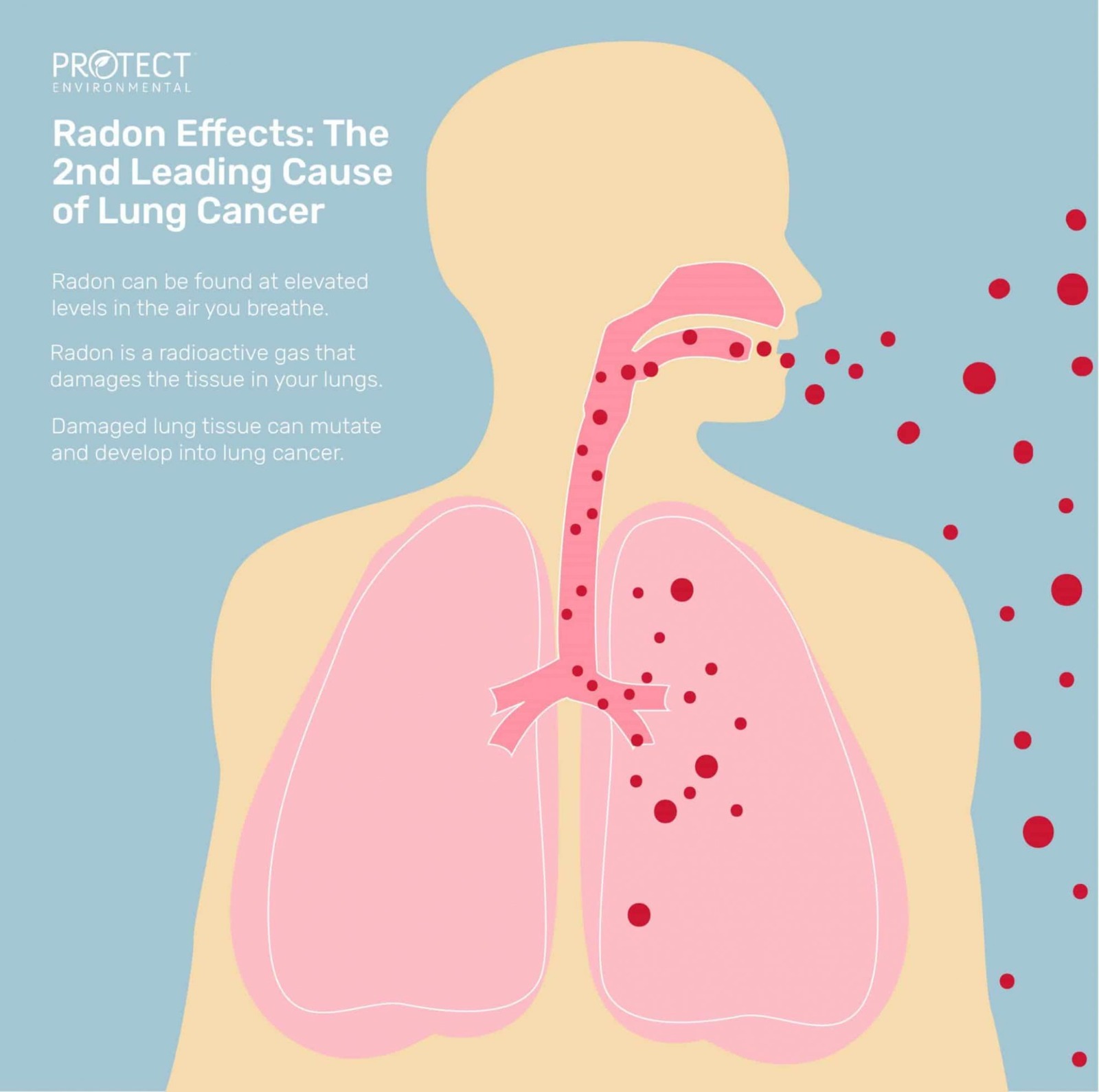
Over time, breathing in high quantities of radon raises your chance of lung cancer.
The leading #1 cause of lung cancer in nonsmokers is radon.
Lung cancer caused by radon claims the lives of about 21,000 Americans each year. Lung cancer risk is significantly increased in smokers who inhale radon.
Where can one find radon gas?
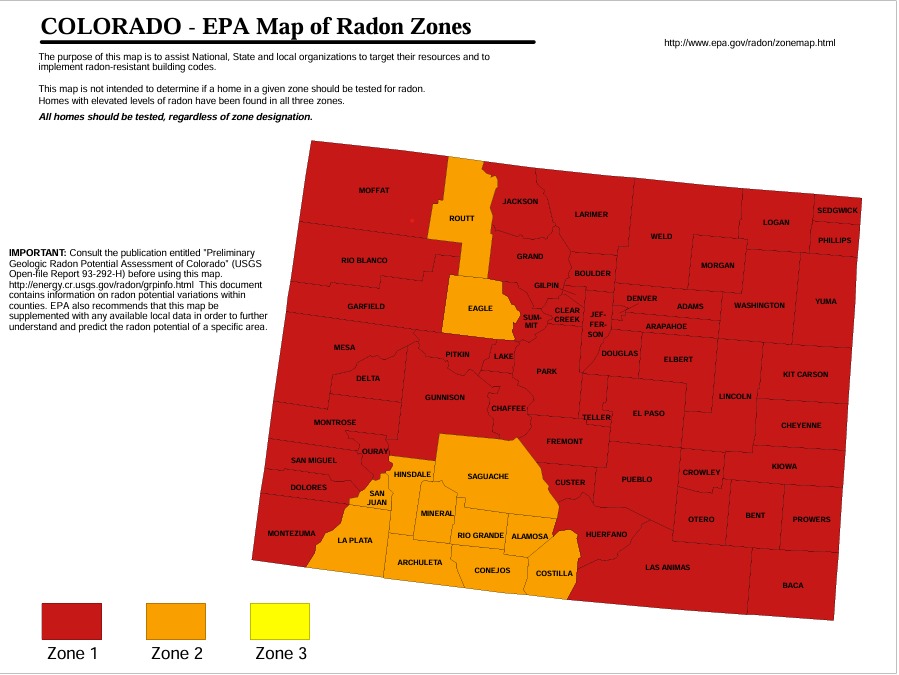
Every state in the United States has radon. Depending on the types of rocks and soil in each location, radon levels and amounts vary across the nation. The majority of exposure for the general public occurs within the house.
Radon levels are usually higher in places that are:
- Closer to the ground, including basements or underground mines.
- Poorly ventilated, typically have greater levels of Radon.
- Completely sealed off with no means of releasing radon.
- Extremely insulated.
What exposes people to radon?
Radon gas is released from radioactive rocks and soil during their breakdown. Construction joints or fractures in walls and floors are two possible entry points for that gas into buildings.
• Foundation gaps close to wiring or pipes.
• Construction materials derived from organic resources, like granite.
• Water, particularly that which is drawn from underground wells.
What signs of exposure to radon are present?
Breathing in background radon radiation or radon decay products (dust particles) does not immediately cause any signs or symptoms.
Is it possible to test for radon in my house?
Indeed. Doing a home test is a crucial step to take, particularly if you reside in a region with higher radon levels.
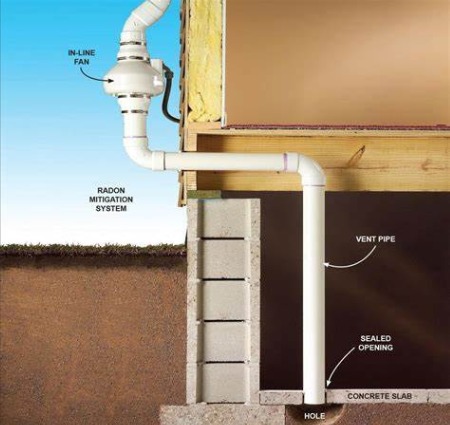
If there is a high radon level, what can I do?
For what are known as radon mitigation services, you should engage a specialist if the building has a high radon level (greater than 148 Bq/m3 or 4 pCi/L). These have the potential to 99% lower radon levels.
• Sub-slab depressurization devices that vent to outside air are among the options.
• Another is air filtering of dust particles containing products of radon decay.
• Plastic sheeting in crawl space-equipped homes.
• Patches for foundation cracks.
• Making ventilation systems inside better.
To learn more, please visit the US Environmental Protection Agency’s “keyword Radon” and the Colorado Citizens Guide to Radon at https://cdphe.colorado.gov/hm/radon.
Wholesome residences finding the radon channels into your house require the greatest caliber of diagnostics, which Healthy Homes Radon Solutions offers. To identify the source of the problem, we employ the most recent technologies such as micro manometers and thermal imaging. After identifying the routes, we build a commonsense system that is tailored to your house. Your entire house is treated, not just the basement. Healthy Homes Radon Solutions is safeguarding your family, and it all begins with a healthy home!

